liver scan
What is a Liver Scan?
A liver scan is a medical imaging test used to assess the structure and function of the liver. It shows the size and shape of your liver and how well the different parts of it are working. It also shows what your spleen is like and how well it works.
There are different liver scans, including ultrasound, CT (computed tomography), MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), and nuclear medicine scans, such as a liver-spleen scan or elastography. Each type serves a specific purpose, from evaluating the liver size and shape to detecting tumours, fibrosis, or fat accumulation.
Who is Suitable for a Liver Scan?
A liver scan is recommended for individuals with suspected liver conditions or those at risk of liver disease. Suitable candidates include:
- Patients with persistent liver-related symptoms such as jaundice, abdominal pain, or unexplained weight loss
- Individuals with a history of liver disease, such as hepatitis B or C, cirrhosis, or fatty liver disease
- People with abnormal liver function test results
- Individuals at high risk of liver cancer, particularly those with long-term liver disease
- Those with a history of excessive alcohol consumption
- Patients being monitored for liver disease progression or treatment response
Benefits of a Liver Scan
A liver scan offers several advantages in diagnosing and managing liver-related conditions, including:
- Early Detection – Helps identify liver disease in its early stages before symptoms become severe
- Non-Invasive – Many liver scans, such as ultrasound and MRI, do not require surgery or extensive procedures
- Accurate Diagnosis – Provides detailed images of liver structure and function to help detect abnormalities
- Monitoring Disease Progression – Helps track changes in liver health over time, especially in chronic conditions
- Guiding Treatment – Assists doctors in planning appropriate treatments and interventions based on scan findings
Conditions Diagnosed by a Liver scan
A liver scan can help diagnose a variety of liver-related conditions, including:
- Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD and AFLD) – Detects excess fat accumulation in the liver
- Liver Cirrhosis – Identifies scarring and damage caused by chronic liver disease
- Hepatitis – Assesses liver inflammation due to viral infections, autoimmune conditions, or other causes
- Liver Tumours and Cancer – Detects benign and malignant growths in the liver
- Liver Fibrosis – Measures the extent of liver scarring, which can indicate disease severity
- Liver Cysts – Identifies fluid-filled sacs in the liver that may require monitoring
- Bile Duct Obstruction – Detects blockages that affect bile flow and digestion
- Liver Abscess – Identifies infections that cause pus-filled pockets in the liver
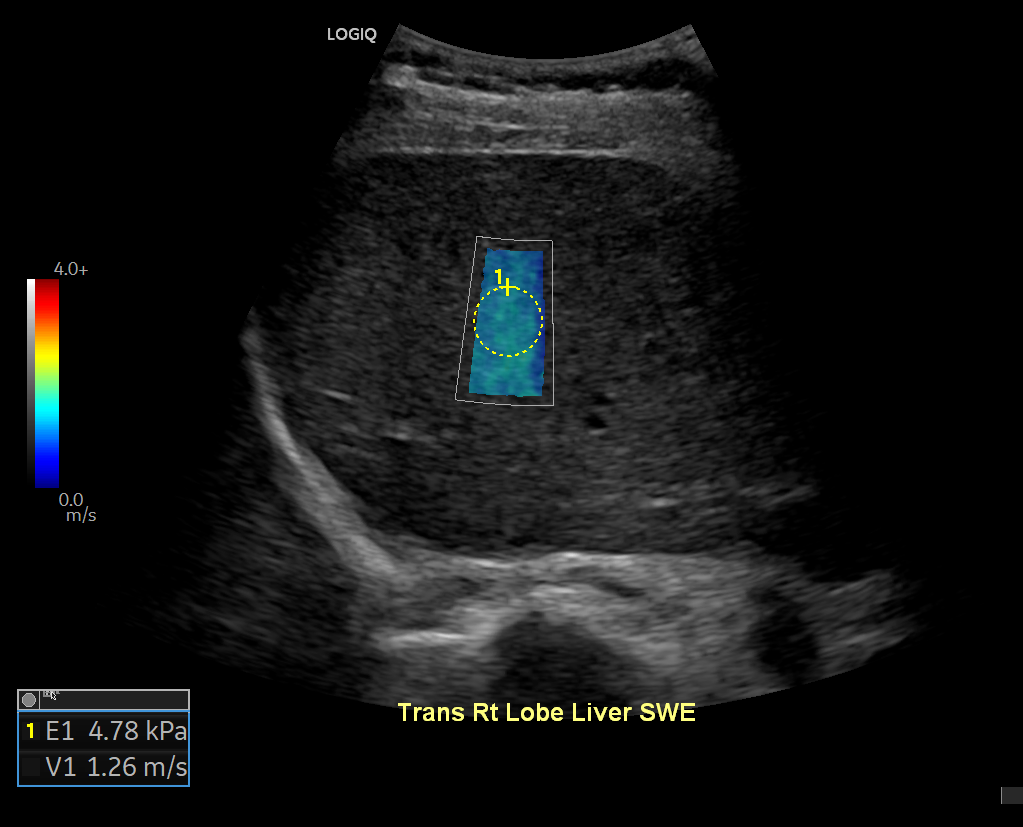
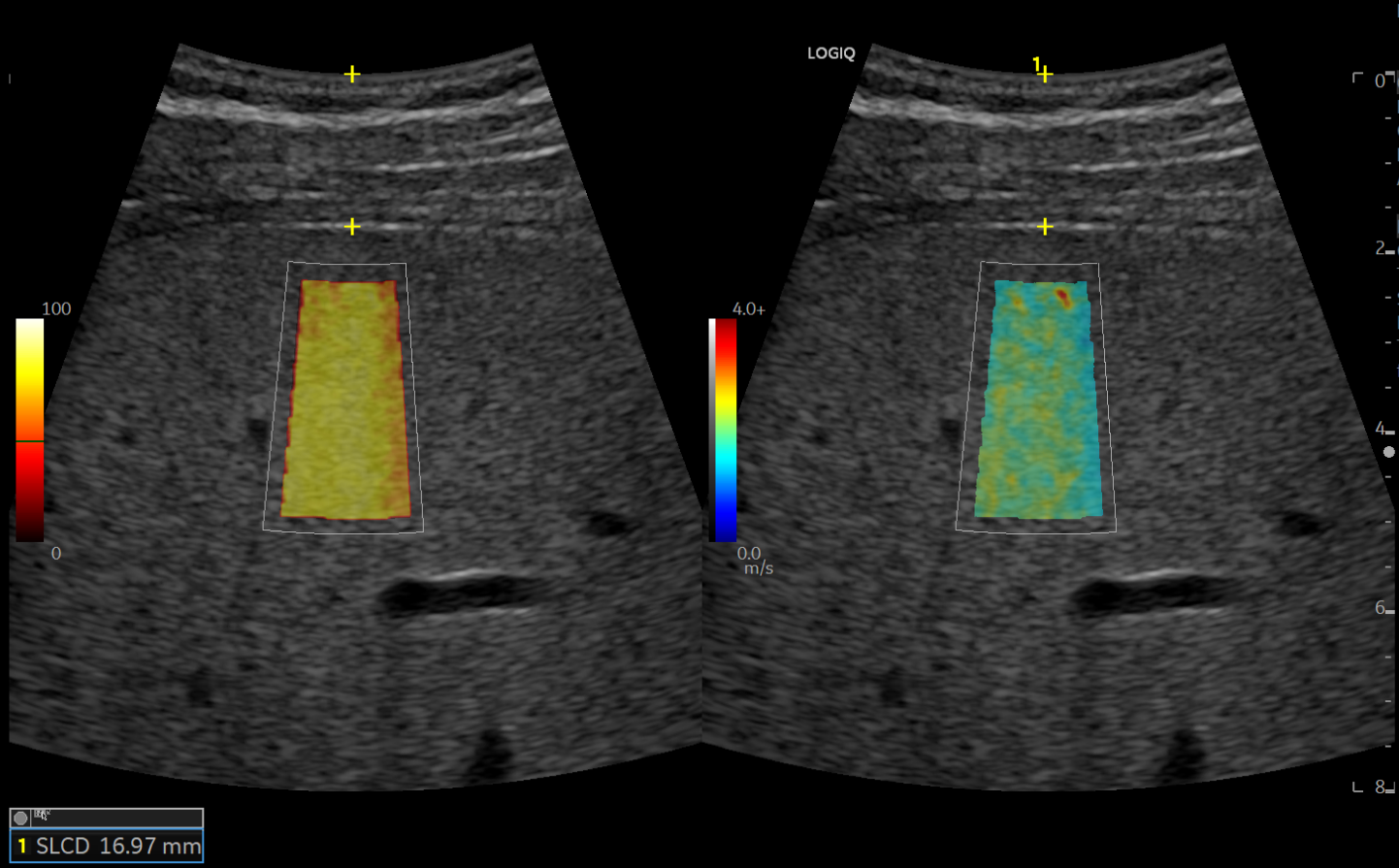
What Further Information Can a Liver Scan Show?
A liver scan provides detailed insights into the liver’s structure, function, and any abnormalities. Depending on the type of scan performed, it can reveal:
- Liver Size and Shape – Helps detect conditions like an enlarged liver (hepatomegaly) or shrunken liver (seen in cirrhosis).
- Fat Content – Identifies fatty liver disease and assesses its severity.
- Fibrosis and Scarring – Measures liver stiffness, which helps diagnose fibrosis or cirrhosis.
- Tumours and Growths – Differentiates between benign and malignant liver tumours.
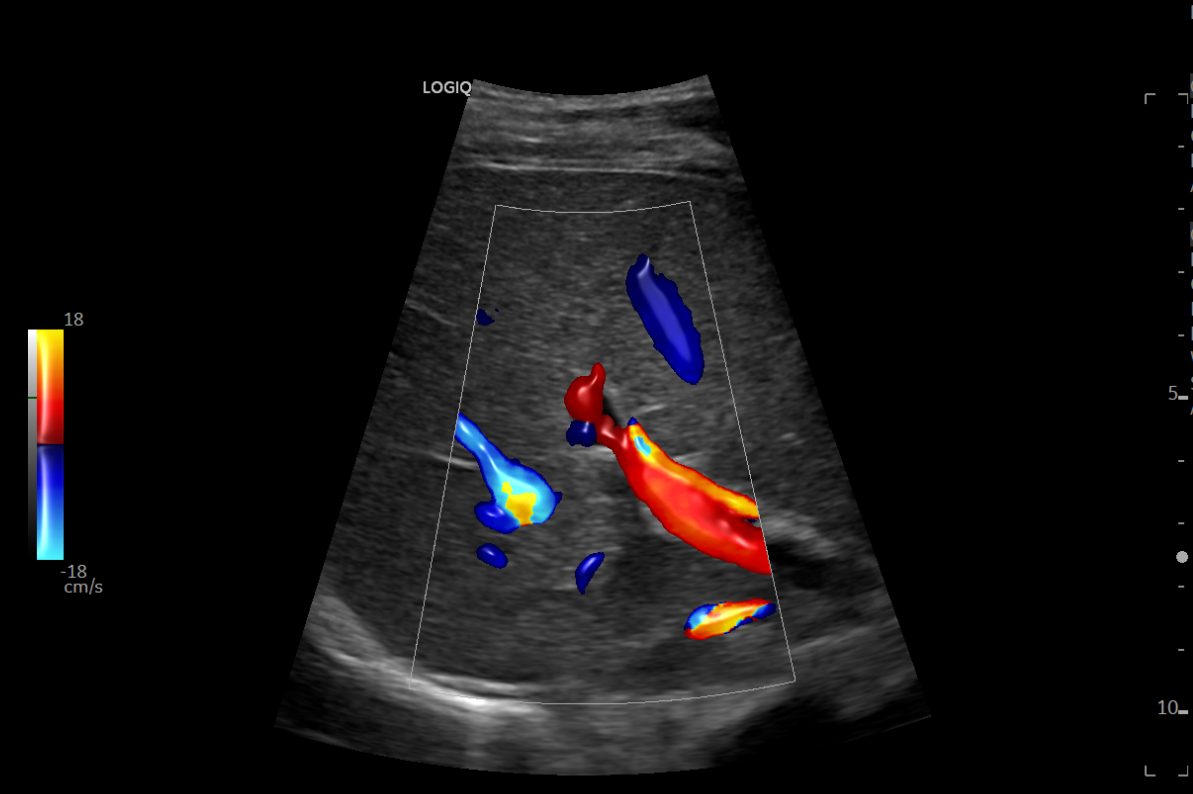
- Blood Flow and Function – Assesses blood circulation within the liver, crucial for detecting conditions like portal hypertension.
- Biliary Tract Abnormalities – Detects blockages or other issues affecting bile flow.
Preparation for a Liver Scan
- What to Bring
- A referral from your doctor.
- Any previous imaging results for comparison.
- Medicare or private health insurance details (if applicable).
- What to Wear
- Loose-fitting, comfortable clothing without metal zippers or buttons (especially for MRI or CT scans).
- Avoid wearing jewellery or accessories around the abdomen.
- Dietary Restrictions
- For some liver scans (such as ultrasound or MRI), fasting for 4–6 hours before the scan may be required.
- Water is usually allowed but check with the imaging center for specific instructions.
- Medication Guidelines
- Continue taking regular medications unless advised otherwise by your doctor.
- Inform the radiology team if you are diabetic or taking blood thinners.
- Duration of the Scan
- Most liver scans take 15 to 60 minutes, depending on the type of imaging used.
Nuclear Medicine Liver-Spleen Scan Procedure
What about the injection?
You are given a small injection into a vein in your arm, and then there is a delay of about 15 minutes before the scan starts. There are no side effects, and you will not feel tired or dizzy. You can drive a car.
What about the pictures?
After the 15-minute delay, several scan pictures of your liver and spleen are taken. This takes about 45 to 60 minutes.
What to Expect After a Liver Scan?
- Post Instructions: You can resume normal activities.
- Receiving Results
- Results will be available the following day after 2 PM.
- If urgent findings are detected, your doctor may contact you sooner.
- Follow-Up
- Depending on the results, your doctor may recommend further tests, lifestyle changes, or treatment.
Liver Scan Prognosis
A liver scan helps detect, diagnose, and monitor liver conditions early, significantly improving prognosis. A timely liver scan enables early intervention, reducing the risk of severe complications and improving long-term health outcomes.
Liver Scan Risks
Liver scans are generally safe, but certain risks may be associated with specific types of imaging:
- Ultrasound – No known risks as it uses sound waves and is non-invasive.
- CT Scan – Exposure to a small amount of radiation, which is generally safe but should be avoided in pregnancy unless essential.
- Contrast Dye Risks – In CT, contrast agents may cause allergic reactions in rare cases. Patients with kidney disease should inform their doctor, as contrast dyes can affect kidney function.
- Nuclear Medicine Scan – Involves a small dose of radiation, which is safe for most people but should be avoided in pregnancy or breastfeeding unless necessary.
What if a Liver Scan is Delayed?
Delaying a liver scan can lead to the progression of undiagnosed conditions, potentially worsening health outcomes. If a liver scan is recommended, it is best to schedule it as soon as possible to avoid complications and begin treatment early if needed.
Liver Scan Costs
- Medicare Coverage:
Bulk billed. No out-of-pocket cost.