HEART IMAGING
STRESS MIBI:
- See under NUCLEAR MEDICINE Heading
CT CALCIUM SCORE
- A coronary artery calcium score is a measurement of the amount of calcium in the walls of the arteries that supply the heart muscle. It is measured by taking a special computed tomography (CT) scan of the heart. The scan shows the amount of hardening of the artery wall (the disease that causes this hardening is called atherosclerosis). The results of the scan make it possible to estimate the risk of a heart attack or stroke (brain attack) in the next 5–10 years. The more calcium (and therefore the more atherosclerosis) there is, the higher the risk of a heart attack or stroke.
- A high calcium score does not mean that you will have a heart attack, only that there is a greater likelihood of having one than someone with a low score. Even a person with a score of zero could have a heart attack.
- On the day of the CT scan of your heart, do not smoke or drink coffee, tea, cola drinks, herbal teas or other caffeine-containing drinks. No other preparation is needed.
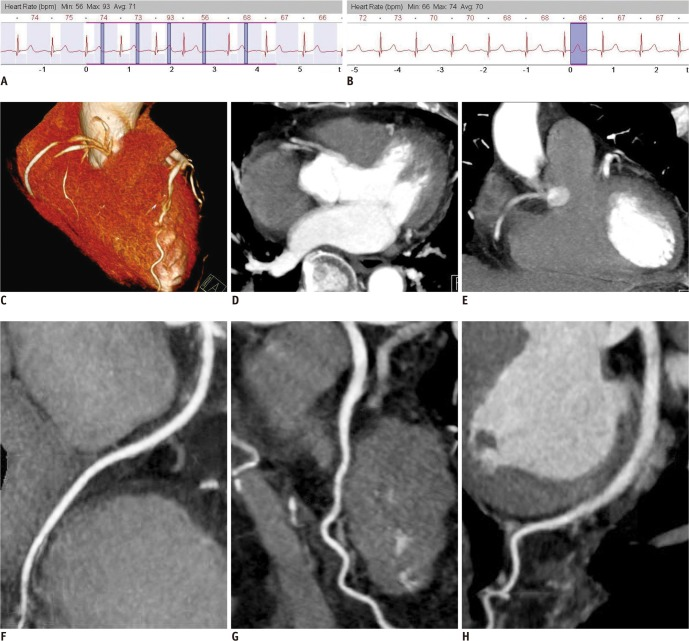
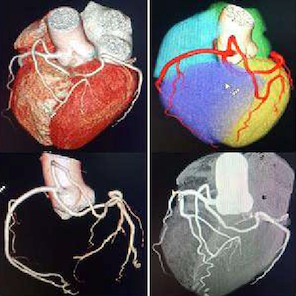
CTCA (CARDIAC ANGIOGRAM)
- CTCA (CARDIAC ANGIOGRAM) is a CT imaging technique used to visualize the coronary arteries (which are the blood vessels that supply the heart muscle with oxygen-rich blood). It provides detailed images of the coronary arteries, similar to a hospital-based coronary angiogram but without the need for invasive procedures. Preparation is required. See below.
Who is Suitable for CTCA?
Heart imaging may be recommended for individuals who:
- Experience symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, or palpitations.
- Have risk factors for heart disease, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, or a family history of heart disease.
- Require assessment before major surgery.
- Have an existing heart condition that needs monitoring.
- Have had a previous heart attack or stroke.
- Are undergoing treatment for heart disease and need to check treatment effectiveness.
Benefits of CTCA
- Early Detection: Identifies heart disease early, improving treatment outcomes.
- Accurate Diagnosis: Helps differentiate between different types of heart conditions.
- Guides Treatment Plans: Provides valuable information for selecting the best treatment approach.
- Monitors Progress: Tracks heart disease progression and evaluates treatment effectiveness.
- Minimally Invasive: Most heart imaging tests are non-invasive or involve minimal discomfort.
What Further Information Can CTCA Show?
- Heart Size and Shape: Identifies enlargement or structural abnormalities.
- Blood Flow Patterns: Assesses circulation efficiency and detects blockages.
- Fluid Buildup: Identifies pericardial effusion (fluid around the heart).
- Plaque Deposits: Detects calcium buildup in coronary arteries.
Preparation for CTCA
- To maintain heart rate < 65 bpm: Metoprolol 50-100mg the night before and 8am morning of CTCA (tablets to be given by our practice OR by your referring doctor) OR take regular Beta blocker / calcium channel blocker as prescribed.
- Fasting: Do not eat or drink anything (except for water) for 4 hours before your appointment
- Caffeine Restriction: Avoid coffee, tea, energy drink, chocolate, and caffeinated sodas for 24 hours before your scan.
- Nicotine and Alcohol: Avoid Smoking and alcohol for 24 hours before the scan.
- Do not take Viagra, Cialis, or Levitra, or similar meditation for 36 hours prior to CTCA scan.
- Medications:
- If you are taking beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, or anti-arrhythmic medications, consult your doctor to discuss whether you should temporarily stop them before the scan.
- Take all morning medication except Metformin.
What to Bring:
- A referral from your doctor.
- Medicare
- A list of current medications.
How Long Does It Take?
- The actual CT scanning will take approximately 20 minutes.
- The whole procedure, including the preparation, scanning and recovery, can take up to 2 hours, particularly if you have been given beta-blockers.
What to Expect After a CTCA?
Immediate Aftercare:
- CTCA: You can resume normal activities after your heart rate and blood pressure are checked by our staff after the scan.
Possible Side Effects:
- Contrast Dye: Some people may experience mild nausea or warmth. Rarely, allergic reactions can occur.
- Radiation Exposure: Minimal, but repeated imaging should be spaced appropriately.
- Injection Site Discomfort: Some bruising or soreness if an IV was used.
- Fatigue: A common temporary effect, especially after stress tests.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
- Severe chest pain or shortness of breath.
- Signs of infection (redness, swelling) at the injection/catheter site.
- Dizziness or fainting.
- Allergic reaction (rash, difficulty breathing).
Heart Imaging Prognosis
The prognosis depends on the findings of the heart imaging test. Possible outcomes include:
- Normal Results: Indicates healthy heart function with no significant blockages or abnormalities.
- Mild Abnormalities: This may suggest early-stage heart disease that can be managed with lifestyle changes.
- Significant Issues: If blockages, valve problems, or structural heart disease are detected, further tests, medication, or procedures like angioplasty or surgery may be required.
- Post-Treatment Monitoring: For conditions such as heart failure, coronary artery disease, or valve disorders, regular follow-ups and repeat imaging may be necessary.
What if a Heart Imaging is Delayed?
- Undiagnosed Heart Disease: Conditions like coronary artery disease (CAD) or valve disorders may worsen if not detected early.
- Increased Risk of Heart Attack or Stroke: Delayed diagnosis of blocked arteries may result in a higher risk of serious cardiac events.
- Unnecessary Symptoms and Discomfort: If imaging is postponed, symptoms like chest pain, fatigue, or breathlessness may persist without explanation.
- Delayed Treatment: Many heart conditions are easier to manage when caught early. A delay may result in the need for more aggressive treatments later.
Heart Imaging Costs
Medicare Coverage
- All Bulk billed. No out-of-pocket costs.
- A referral from a GP or specialist is required for Medicare rebates.